DE-4000 SCRIPTING REFERENCE MANUAL
There is a delicate balance between providing a system that has capabilities that can be configured through a fixed set of options, and one that can be extended and expanded with custom programming. In designing the DE-4000 control system, the choice was made to provide a system where most applications can be met with simple configuration, but advanced functionality can be provided through custom programming using the “Lua” language.
Lua is often referred to as a scripting language. Scripting languages differ from compiled languages as they eliminate extra step of compiling the written program into machine code.
Lua comes with a background of being robust, fast, and geared towards embedded applications, with a proven track record in the gaming industry. For the DE-4000 system it is small and fits in the memory we have available, holds a lot of power, and keeps it simple for writing in the language. All information regarding the Lua scripting language is located at https://Lua.org Using the Lua engine as an embedded tool allows for taking advantage of a full architecture and standard at your fingertips. Within the language there are all of the normal attributes to programming such as functions, variables, statements, expressions etc. All of this reference material can be found at https://lua.org/ manual/5.3/ For getting started and using a guided reference, there are several editions of “Programming in Lua” available. Most recent editions are a paid for product that come in paper back or ebook form. While testing out Lua and becoming familiar, a free first edition is available and covers a lot of learning needs to get comfortable with the language. It can be located at https://www.lua.org/pil/contents.html. A major advantage to using Lua is its inherent ability to allow custom functions. While all normal functions and calls are published, there is the ability to add new functions in the DE-4000 firmware. Once new functions are defined and have calls to their internal properties, they then can be published for the user. This includes functions such as our flexible Modbus table and talking with various terminal boards linked in the system. Below is the start to the list of Altronic based functions. As functionality and features come to life through new ideas, this document will continually get updated with the latest scripts that we make available.
GETTING STARTED WITH DE-4000 SCRIPTS Basic Scripting on DE-4000
Begin on Dashboard on DE-4000 system environment
Choose “Global” from menu on left side of screen
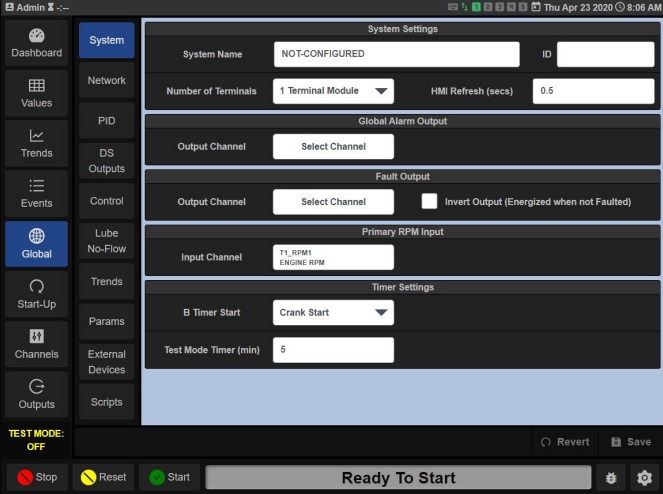
In the Sub-Menu on the Left side select “Scripts”
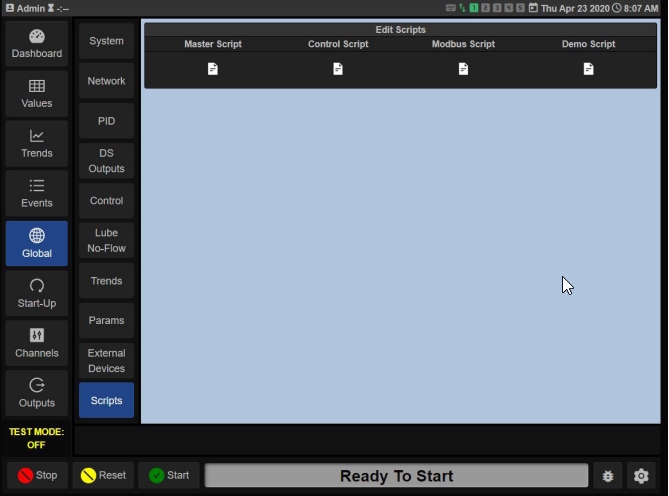
Select one of the page icons under one of the 4 script options to open editor
Scripting can be entered into the editor
Scripting Windows and examples
Master Script
The Master Script section is the Primary scripting environment. Primary scripting functions can be written in this section.
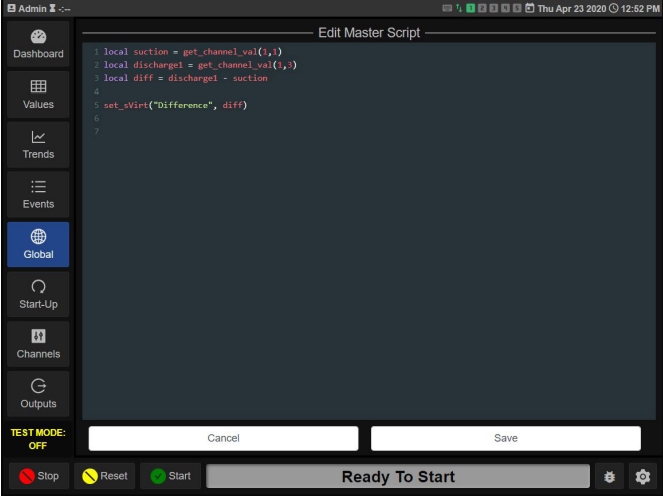
Example:
local suction = get_channel_val(1,1)
local discharge1 = get_channel_val(1,3)
diff = discharge1 - suction
set_sVirt(“Difference”, diff)The first line gets the channel value from Terminal board 1 Input 1 and stores it in local variable named suction. The second line gets the channel value from Terminal board 1 Input 3 and stores it in local variable named discharge1. The third line takes the discharge1 pressure and subtracts the suction pressure and stores it in the global variable named diff (NOTE: Any value that you want to access from another scripting section must be stored in a global variable. This is used most in calling values into Modbus registers as explained below). The fourth line copies the value from diff and stores it into the Virtual status channel named “Difference” This channel can be displayed on the Dashboard.
Control Script
The Control Script section is used to override the default control strategy found on the Global/Control page. A copy of the default control script (found in attached appendix) can be copied into this section and then modified to change the control functionality as well as add additional control loops beyond the default 2.
Modbus Script
The Modbus Script section is used to move data into and out of Modbus registers
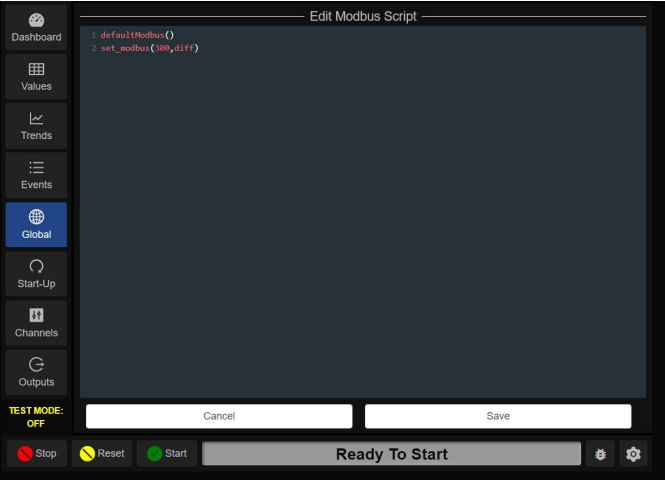
defaultModbus()
set_modbus(300,diff)The first line pulls in the factory set Modbus mapping The second line moves the value from the global variable named diff into the 40300 Modbus Register
DE-4000 Lua Script API
CUSTOM FUNCTIONS FOR SCRIPTING
create_param(“index”,default,”catergory”,”description”)
-
creates a user configurable parameter
-
parameter is stored as
index, -
default value(If not changed by user) is
default -
parameters will be grouped on the Global/Params page by
category -
descriptionis text to describe the parameter to the user
Example:
create_param("NumEngCyl",8,"Engine Params","Num. of Engine Cylinders")
get_channel_val(terminal,channel)
-
returns current value of analog input
channelon terminal moduleterminal -
return value type is numeric
Example:
local sp = get_channel_val(1,5)
reads value of Suction Pressure from Terminal Module #1 , Input #5get_gbl(“index”,default)
-
returns global config setting stored under
indexor returnsdefaultif not definednote: get_gbl is used to retrieve global CONFIGURATION settings that are typically set when the system is configured and do not change as the system is running. If you want to set and retrieve global STATUS variables use the get_sGbl() and set_sGbl() functions >If you want to create and read virtual channels use the set_sVirt() and get_sVirt() functions.
Example:
local nt = get_gbl("NumTerm",1)
gets the number of terminal boards installed in the system
get_param(“index”)
-
return either the default value or the user configured value of the parameter
index
Example:
get_param("NumEngCyl")
>gets the configured parameter for number of engine cylinders
get_rpm(channel)
- reads the RPM input
channelin units of revolutions per minute
note: valid channel numbers are 1 – 10(2 channels per board, up to 5 terminal boards)
Each Terminal Module has 2 RPM inputs (RPM1 and RPM2)
-
Terminal Module #1 RPM channels are 1,2
-
Terminal Module #2 RPM channels are 3,4
-
Terminal Module #3 RPM channels are 5,6
-
Terminal Module #4 RPM channels are 7,8
-
Terminal Module #5 RPM channels are 9,10
Example:
local engineRPM = get_rpm(1)
local turboRPM = get_rpm(6)Read RPM1 channel from terminal module #1 and read RPM2 channel from Terminal module #3
get_sGbl(“index”, default)
-
If
indexis defined in the global status table then it returns the value associated withindex -
If
indexis not defined and optionaldefaultis provided then returnsdefault
>note: It is recommended to always provide a default value when using this function
Example:
local cp = get_sGbl("calculatedPressure",0)
get the previously stored value “calculatedPressure”, Returns
0if not found.
get_state()
-
returns the current engine state(possible values currently 0 – 10)
Example:
local engineState = get_state()
if engineState > 7 then
set_timer("WarmupTimer",1000)
end
get_sVirt(“index”)
-
returns the value of virtual channel
indexor returnsdefaultif the virtual channel does not exist.
Example:
local tl = get_sGbl("timeLimit")
local et = get_sVirt("ElapsedTime",0)
if et > tl then
set_sGbl("timeExceeded",true)
else
set_sGbl("timeExceeded",false)
endGets the value of virtual channel ElapsedTime and set value of status global “timeExceeded” if ElapsedTime is greater than status global “timeLimit”
get_time()
-
returns the UNIX “epoch” time (Defined as the number of seconds elapsed since Jan 1, 1970)
Example:
local startTime = get_sGbl("startTime",0)
if startTime == 0 then
local currentTime = get_time()
startTime = currentTime
set_sGbl("startTime",currentTime)
end
local et = get_time() - startTime
set_sVirt("ElapsedTime",et)Stores current time if first time through, otherwise calculate elapsed time
get_timer(“index”)
-
returns 1 or 2 values
-
First return value(Boolean) is true if timer is active(counting down) or false if timer is expired or has not been set yet
-
Second return value is the number of seconds remaining or -1 if timer is not active or has not been set yet
Example:
if not get_timer("myTimer") then
set_sGbl("timedOut",true)
else
set_sGbl("timedOut",false)
endif timer is expired, then set global status “timedOut” to true
local active,remaining = get_timer("myTimer")
if not active then
set_sVirt("timeRemaining","Expired")
else
set_sVirt("timeRemaining",remaining)
endgetStateLabel(state)
-
return the label for the engine state corresponding to the parameter
state
Example:
local stateLabel = getStateLabel(get_state())
local active, remaining = get_timer("myTimer")
if remaining > 0 then
stateLabel == StateLabel.." "..remaining
end
set_sVirt("Countdown",stateLabel)set_sGbl(“index”,value)
-
store
valuein the global status table underindex -
value can be a number or string but if storing a boolean use the tostring() function
Example:
local mpe = false
local sp = get_channel_val(1,5)
if sp > 15 then
mpe = true
end
set_sGbl("minPressureExceeded",tostring(mpe))store boolean value minPressureExceeded
set_sVirt(“index”,value)
-
sets a virtual status channel with channel name
indexNote: Once you create a virtual channel, you can add that channel to the dashboard using the channel name
index
Example:
local sp = get_channel_val(1,5) --suction pressure
local dp = get_channel_val(1,6) --discharge pressure
local diffPress = dp - sp
set_sVirt("SuctDischDiff",diffPress)calculate the differential between suction and discharge pressure and assign to virtual channel
set_timer(“index”,secs)
-
activate timer
indexand set countdown time tosecs
Example:
set_timer("myTimer",300)
create timer
myTimerand start countdown time to 300 seconds
Master Control Script
When you enter a control setup under the Global Control page the code that runs is called MasterControl.
If you wish to modify this functionality you can copy this code into the Control Script editor and make your changes to the standard configuration.
local rampRate1 = get_gbl("rampRate1",0.8)
local rampRate2 = get_gbl("rampRate2",0.8)
local dischTerm = tonumber_def(get_gbl("spDischTerm",0),0)
local dischChan = tonumber_def(get_gbl("spDischChan",0),0)
local suctTerm = tonumber_def(get_gbl("spSuctTerm",0),0)
local suctChan = tonumber_def(get_gbl("spSuctChan",0),0)
local suctMin = tonumber_def(get_gbl("suctMin",0),0)
local recycleMin = tonumber_def(get_gbl("recycleMin",0),0)
local recycleMax = tonumber_def(get_gbl("recycleMax",0),0)
local suctSp = tonumber_def(get_gbl("suctSp",0),0)
local dischMax = tonumber_def(get_gbl("dischMax",0),0)
local dischSp = tonumber_def(get_gbl("dischSp",0),0)
local outputTerm = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputTerm",0),0)
local outputChan = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputChan",0),0)
local recycleTerm = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputTerm2",0),0)
local recycleChan = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputChan2",0),0)
local speedRevAct = tonumber_def(get_gbl("speedRevAct",0),0)
local recycleRevAct = tonumber_def(get_gbl("recycleRevAct",0),0)
local outputLow = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputLow",0),0)
local outputLow2 = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputLow2",0),0)
local outputHigh = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputHigh",0),0)
local outputHigh2 = tonumber_def(get_gbl("outputHigh2",0),0)
local spSuctType = get_gbl("spSuctType","linear")
local spDischType = get_gbl("spDischType","linear")
local suctPIDPFactor = tonumber_def(get_gbl("suctPIDPFactor",0),0)
local suctPIDIFactor = tonumber_def(get_gbl("suctPIDIFactor",0),0)
local suctPIDDFactor = tonumber_def(get_gbl("suctPIDDFactor",0),0)
local dischPIDPFactor = tonumber_def(get_gbl("dischPIDPFactor",0),0)
local dischPIDIFactor = tonumber_def(get_gbl("dischPIDIFactor",0),0)
local dischPIDDFactor = tonumber_def(get_gbl("dischPIDDFactor",0),0)
local recycleCtrl = false
local recycleSuctionRev = false
local recycleDischargeRev = false
if recycleChan > 0 and recycleTerm > 0 then
recycleCtrl = true
end
local dischPct = 100
local suctPct = 100
local dischOutput = 0
local suctOutput = 0
local rSuctOutput = 0
local rDischOutput = 0
local minLoad = 0
local maxLoad = 100
local minRecycle = 0
local maxRecycle = 100
local speedTarget = get_sGbl("speedTarget",0)
local recycleTarget = get_sGbl("recycleTarget",0)
function map_range(rangeLow,rangeHigh,input)
if input <= rangeLow and input <= rangeHigh then
return 0
end
if input >= rangeLow and input >= rangeHigh then
return 100
end
local rangeDiff = math.abs(rangeLow - rangeHigh)
local min = math.min(rangeLow,rangeHigh)
local retval = math.abs(input - min) / rangeDiff * 100
if retval > 100 then retval = 100 end
if retval < 0 then retval = 0 end
return retval
end
local suct = false
local suctVal = 0
if tonumber_def(get_gbl("spSuctEn",0),0) == 1 then
if suctTerm > 0 and suctChan > 0 then
suctVal = get_channel_val(suctTerm,suctChan)
suct = true
end
end
if suct then
if spSuctType == "linear" then
local suctDiff = suctSp - suctMin
if suctDiff == 0 then suctDiff = 1 end
if suctVal < suctSp then
local suctErr = suctSp - suctVal
suctPct = suctErr / suctDiff
if suctPct > 1 then suctPct = 1 end
if suctPct < 0 then suctPct = 0 end
suctOutput = (1 - suctPct) * 100
else
suctOutput = 100
end
else
set_gbl("PIDsuctEnable",1)
set_gbl("PIDsuctPFactor",suctPIDPFactor)
set_gbl("PIDsuctIFactor",suctPIDIFactor)
set_gbl("PIDsuctDFactor",suctPIDDFactor)
set_gbl("PIDsuctSp",suctSp)
set_gbl("PIDsuctDeadband",0.2)
local suctPidOutput = doPid("suct",suctVal)
suctOutput = suctPidOutput
end
else
suctOutput = 100
end
local disch = false
local dischVal = 0
if tonumber_def(get_gbl("spDischEn",0),0) == 1 then
if dischTerm > 0 and dischChan > 0 then
dischVal = get_channel_val(dischTerm,dischChan)
disch = true
end
end
if disch then
if spDischType == "linear" then
local dischDiff = dischMax - dischSp
if dischDiff == 0 then dischDiff = 1 end
if dischVal > dischSp then
local dischErr = dischVal - dischSp
dischPct = dischErr / dischDiff
if dischPct > 1 then dischPct = 1 end
if dischPct < 0 then dischPct = 0 end
dischOutput = (1 - dischPct) * 100
else
dischOutput = 100
end
else
set_gbl("PIDdischEnable",1)
set_gbl("PIDdischPFactor",dischPIDPFactor)
set_gbl("PIDdischIFactor",dischPIDIFactor)
set_gbl("PIDdischDFactor",dischPIDDFactor)
set_gbl("PIDdischSp",dischSp)
set_gbl("PIDdischRevAct",1)
set_gbl("PIDdischDeadband",0.2)
local dischPidOutput = doPid("disch",dischVal)
dischOutput = dischPidOutput
end
else
dischOutput = 100
end
local minOutput = 100
local winning = 0
if suctOutput < minOutput then
minOutput = suctOutput
winning = 1
end
if dischOutput < minOutput then
minOutput = dischOutput
winning = 2
end
if suctOutput == dischOutput then
winning = 0
end
if winning == 0 then
set_gbl("PIDsuctMax",100)
set_gbl("PIDdischMax",100)
end
if winning == 1 then
set_gbl("PIDdischMax",math.min(suctOutput + 2,100))
set_gbl("integraldisch",0)
set_gbl("lastErrdisch",0)
set_gbl("outputSumdisch",0)
set_gbl("PIDsuctMax",100)
end
if winning == 2 then
set_gbl("PIDsuctMax",math.min(dischOutput + 2,100))
set_gbl("integralsuct",0)
set_gbl("lastErrsuct",0)
set_gbl("outputSumsuct",0)
set_gbl("PIDdischMax",100)
end
local recycleMinOutput = minOutput
local manOutput = 0
--********************************************************************
local manMode = 0
local manTerm = tonumber_def(get_gbl("manTerm",0),0)
local manChan = tonumber_def(get_gbl("manChan",0),0)
if manTerm > 0 and manChan > 0 then
local manInput = get_channel_val(manTerm,manChan)
if manInput > 0.5 then
manMode = 0
set_sVirt("SpeedControl","Auto")
else
manMode = 1
set_sVirt("SpeedControl","Manual")
end
else
if get_sVirt("SpeedControl","Auto") == "Auto" then
manMode = 0
else
manMode = 1
end
end
--if manMode == 1 and get_state() == 8 then
local manSpeed = get_sVirt("ManualSpeed",0)
local idleSpeed = get_gbl("idleSpeed",0)
local lowSpeed = get_gbl("lowSpeed",0)
local highSpeed = get_gbl("highSpeed",0)
local maxSpeed = get_gbl("maxSpeed",0)
local diff = highSpeed - lowSpeed
if diff < 0 then diff = 0 end
local maxDiff = maxSpeed - idleSpeed
if maxDiff < 0 then maxDiff = 0 end
if get_sVirt("speedBump",0) ~= 0 then
local si = get_gbl("SpeedIncrement",0)
local sip = get_param("SpeedIncrement",0)
if sip ~= 0 then si = sip end
manSpeed = manSpeed + (si * get_sVirt("speedBump",0))
set_sVirt("speedBump",0)
end
if get_sVirt("AutoManBump",0) > 0 then
set_sVirt("SpeedControl","Auto")
set_sVirt("AutoManBump",0)
end
if get_sVirt("AutoManBump",0) < 0 then
set_sVirt("SpeedControl","Manual")
set_sVirt("AutoManBump",0)
end
if manMode == 1 then
local manSpeedTerm = tonumber_def(get_gbl("manSpeedTerm",0),0)
local manSpeedChan = tonumber_def(get_gbl("manSpeedChan",0),0)
if manSpeedTerm > 0 and manSpeedChan > 0 then --*** USE SPEED POT TO SET SPEED
local speedInput = tonumber(get_channel_val(manSpeedTerm,manSpeedChan))
local speedPct = (speedInput / 5) * 100
if speedPct > 100 then speedPct = 100 end
if speedPct < 0 then speedPct = 0 end
manOutput = speedPct
manSpeed = math.floor((speedPct / 100) * diff + lowSpeed + 0.5)
else -- Use ManualSpeed to set speed
manOutput = ((manSpeed - lowSpeed) / diff) * 100.0
if manOutput < 0 then manOutput = 0 end
if manOutput > 100 then manOutput = 100 end
end
minOutput = manOutput
else
--speedTarget =
local stRpm = (speedTarget/100) * maxDiff + idleSpeed
if stRpm < lowSpeed then stRpm = lowSpeed end
if stRpm > highSpeed then stRpm = highSpeed end
manSpeed = math.floor(stRpm)
end
if manSpeed < lowSpeed then
manSpeed = lowSpeed
end
if manSpeed > highSpeed then
manSpeed = highSpeed
end
set_sVirt("ManualSpeed",manSpeed)
--********************************************************************
local output1 = 0
local output2 = 0
if spSuctType == "pid" or spDischType == "pid" then
output1 = map_range(outputLow,outputHigh,minOutput)
set_sVirt("out1",output1)
output2 = map_range(outputLow2,outputHigh2,recycleMinOutput)
set_sVirt("out2",output2)
local hasRPM = idleSpeed > 0 and lowSpeed > 0 and highSpeed > 0 and maxSpeed > 0
if outputTerm and outputChan then
if hasRPM then
local speedRpm = output1 / 100 * (highSpeed - lowSpeed) + lowSpeed
speedTarget = (speedRpm - idleSpeed) / (maxSpeed - idleSpeed) * 100
else
speedTarget = output1
end
end
if recycleTerm and recycleChan then
set_ao_val(recycleTerm,recycleChan,output2)
end
if get_state() == 9 then
speedTarget = get_sGbl("speedTarget",0)
if speedTarget > 0 then speedTarget = speedTarget - rampRate1 end
if speedTarget < 0 then speedTarget = 0 end
end
if get_state() < 8 then speedTarget = 0 end
set_sGbl("speedTarget",speedTarget)
set_ao_val(outputTerm,outputChan,speedTarget)
set_sVirt("spTarget",speedTarget)
if hasRPM then
local sRpm = (speedTarget/100) * maxDiff + idleSpeed
set_sVirt("Speed Target",math.floor(sRpm + 0.5))
end
else
-- Remember that minOutput is 0 - 100 pct of lowSpeed <-> highSpeed
-- We need to convert this to 0 - 100 pct of idleSpeed <-> maxSpeed
local suctPct = map_range(outputLow,outputHigh,minOutput)
local speedRpm = suctPct / 100 * (highSpeed - lowSpeed) + lowSpeed
minOutput = (speedRpm - idleSpeed) / (maxSpeed - idleSpeed) * 100
if minOutput <= speedTarget then
speedTarget = speedTarget - rampRate1
if speedTarget < minOutput then speedTarget = minOutput end
else
speedTarget = speedTarget + rampRate1
if speedTarget > minOutput then speedTarget = minOutput end
if speedTarget > maxLoad then speedTarget = maxLoad end
end
if speedTarget > maxLoad then speedTarget = maxLoad end
if speedTarget < minLoad then speedTarget = minLoad end
if recycleCtrl then
local recyclePct = map_range(outputLow2,outputHigh2,recycleMinOutput)
if recyclePct <= recycleTarget then
recycleTarget = recycleTarget - rampRate2
if recycleTarget < recyclePct then recycleTarget = recyclePct end
else
recycleTarget = recycleTarget + rampRate2
if recycleTarget > recyclePct then recycleTarget = recyclePct end
end
if recycleTarget > maxRecycle then recycleTarget = maxRecycle end
if recycleTarget < minRecycle then recycleTarget = minRecycle end
local recycleOutput = recycleTarget
if get_state() < 8 then
recycleTarget = 0
end
if recycleRevAct == 1 then
recycleOutput = 100 - recycleOutput
end
set_ao_val(recycleTerm,recycleChan,recycleOutput)
set_sGbl("recycleTarget",recycleTarget)
set_sVirt("recycleTarget",recycleTarget)
end
if get_state() == 9 then
speedTarget = get_sGbl("speedTarget",0)
if speedTarget > 0 then speedTarget = speedTarget - rampRate1 end
if speedTarget < 0 then speedTarget = 0 end
end
if get_state() < 8 then speedTarget = 0 end
set_sGbl("speedTarget",speedTarget)
set_ao_val(outputTerm,outputChan,speedTarget)
set_sVirt("spTarget",speedTarget)
local sRpm = (speedTarget/100) * maxDiff + idleSpeed set_sVirt("Speed Target",math.floor(sRpm + 0.5))
end
Handling Special Characters in Strings
When scripting in Lua for the DE-4000 system, it is important to correctly handle special characters within strings to prevent errors. This is especially critical when passing strings to functions like Custom Fault and others.
Special Characters in Strings
Non-alphanumeric characters, such as %, “, and others, can cause issues in Lua if not properly escaped. Below are some common cases and their solutions.
- Escaping the % Character
- Issue: The % symbol is treated as a special character in Lua and needs to be escaped.
Solution: Use %% to represent a literal % in a string.
Example: Escaping %
local faultMessage = "Current value is 50%% over the limit."
custom_fault(faultMessage)
- In this example, %% ensures that the % is displayed as a literal percentage sign.
Best Practices for Strings with Special Characters
- Always escape non-alphanumeric characters when constructing strings for Lua functions.
- Review strings passed to critical functions like custom_fault or similar to ensure all special characters are properly escaped.
Summary
- Use %% for %, double quotes (“”) for “, and backslashes (\\) for \.
- Follow Lua’s conventions for escaping special characters to ensure robust script execution.
- Consider implementing automated escaping in custom functions to simplify user scripting efforts.